Dental implant surgery is a safe and efficient way to replace a missing tooth, but it can fail if the area around them gets infected. If you have gum disease, you’re at an increased risk of having dental implant surgery fail. This is why it’s important to treat gum disease before getting implants.
If you’ve been diagnosed with gum disease and your dentist recommends dental implants as a solution, make sure you seek dental treatment for your gum disease first. This is because treating gum disease can reduce the likelihood of infection or complications that could result from surgery.
Gum Disease: What Is It and How Can You Get Rid of It?
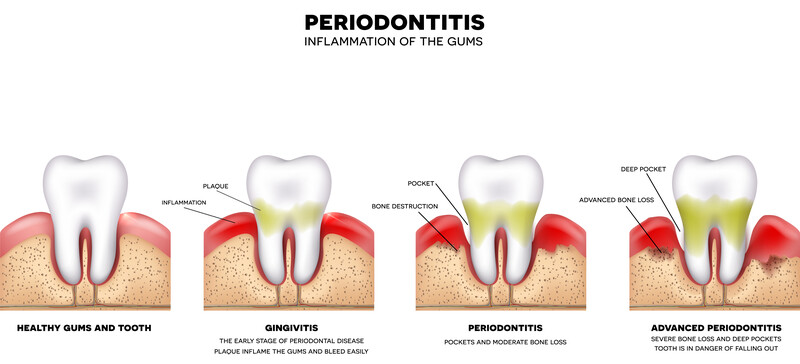
Gum disease is an infection in your gum and bone. Signs of gum disease include redness, swelling, bleeding, and green dental plaque. Gum disease can weaken the jawbone and develop into serious health issues like heart problems or diabetes. The signs of gum disease do not go away on their own; treatment is needed to improve daily quality of life and restore normal health and function.
What Causes Gum Disease
Gum disease is caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that sticks to your teeth and forms up to two days after brushing. It’s mainly caused by poor dental hygiene — not visiting the dentist every six months for routine check-ups and teeth cleaning (known as scaling and root planing) is the main cause of gum disease. A diet high in certain types of sugar can also contribute to gum disease, so it’s important to maintain good eating habits and regular brushing. Gum disease is common among smokers, so smoking can also play a part in its development.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
If you have early-stage signs of gum disease, you might not show any signs of it. Most people know when they need to see their dentist because the pain and discomfort become too much to handle.
For mild gum disease, your gums might bleed or become red when you brush your teeth; this is known as gingivitis. Once plaque has formed on your teeth, it creates a substance called tartar. If you have advanced-stage gum disease, tartar can cause your gums to recede and become sensitive. This causes a small gap between the base of your teeth and your gums.
If left untreated, you might need antibiotics or surgery to treat chronic periodontitis and experience a variety of health issues including cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
Diagnosing Gum Disease
Your dentist can diagnose gum disease using a number of tests and exams. Your dentist will examine your gums to check for redness, swelling, and bleeding. This is known as a gingival bleeding index (GBI). If it’s positive or zero, this means you have healthy or no gum disease and that there are no signs of bleeding. If your GBI score is higher, it means you have serious gum disease and need to see a periodontist, an oral surgeon or tooth implant dentist for treatment straight away.
Your dentist will also ask how long you’ve had the symptoms before diagnosing gum disease. The longer you wait before seeking treatment, the more likely you are to develop periodontitis and other potential complications.
Treating Gum Disease Before Dental Implant Surgery
If you suffer from gum disease, you’re at an increased risk of having dental implant surgery fail. This is why it’s important to treat gum disease before getting implants. Your dentist can treat your gum disease using deep scaling. During treatment, your dentist will clean underneath your gums to remove all the plaque and tartar that has built up over time.
Your dentist may also prescribe you antibiotics to kill any dangerous bacteria growing on your teeth. If you have periodontitis, your dentist might suggest surgery, where they will cut away the diseased tissue to give your gums more space.
Once the gum disease is gone, your dentist will take a CT scan of your jawbone to see if it’s strong enough for implants. If it isn’t, you might need to wait a few months before having surgery because, during those months, your jawbone will heal and prepare for a successful implant procedure.
Preventing gum disease after dental implant surgery
If you’ve recently had dental implants, it’s important to follow good oral hygiene practices to prevent gum disease. This means brushing your teeth at least twice a day, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing at least once a day.
It’s also important to see your dentist every six months for a routine check-up and teeth cleaning (known as scaling and root planing). During this visit, your dentist will clean underneath your gums to remove all the plaque and tartar that has built up over time.
So, can you have dental implants if you suffer from gum disease? Yes, you can. However, it’s important to treat the gum disease before getting implants. Dental implants can be a safe and efficient way to replace a missing tooth, but they can fail if the area around them gets infected. If you suffer from gum disease, it’s important to treat the gum disease before getting implants.
Shirley Mist has been involved in fashion and design for many years. She has also written extensively for many online publications. She currently writes for The Tribune World and is a valued member of our team.